Nature is an enigmatic realm filled with diverse survival strategies, and the animal kingdom showcases a myriad of mysteries. One such puzzling phenomenon is the ability of elephants to survive with a broken leg, while horses face a grim fate when confronted with a similar injury. In this article, we delve into the remarkable self-healing abilities of elephants and the challenges that hinder horses from overcoming broken limbs.
Self-healing Abilities of Elephants:
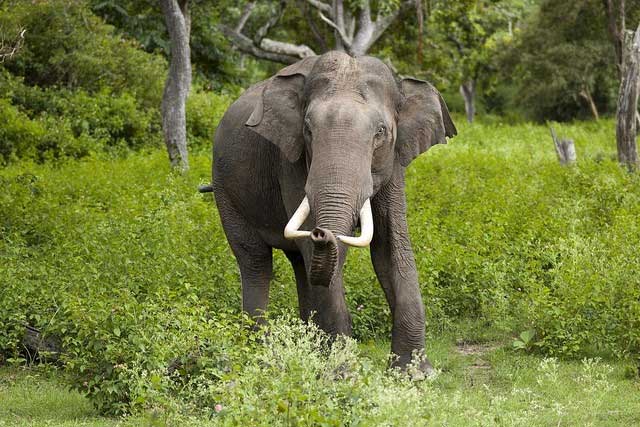

Elephants, as one of the largest land animals, possess extraordinary self-healing capabilities and adaptive mechanisms, particularly when facing the adversity of a broken leg. The foundation of their resilience lies in the unique structure of their bones. Elephant bones are robust yet delicately designed, enabling them to support their immense weight efficiently and reducing strain on other joints during serious injuries like broken legs. Additionally, the abundance of calcium and minerals in their bones accelerates the healing process.
The muscular system of elephants plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and stability. Thick and strong muscles provide the necessary strength to distribute weight evenly across the remaining three legs, reducing pressure on the injured limb. The flexibility and elasticity of their muscle tissue contribute to a smoother recovery process.
Intelligence and sociability further enhance the healing abilities of elephants. These intelligent creatures form a protective circle around an injured companion, offering safety and support. Cooperative efforts ensure that injured elephants receive assistance in finding food and water, facilitating a speedy recovery. The adaptive mechanisms of elephants allow them to quickly adjust to new physical limitations, maximizing their survival and mobility despite losing a leg.
Causes and Limitations for Horses:
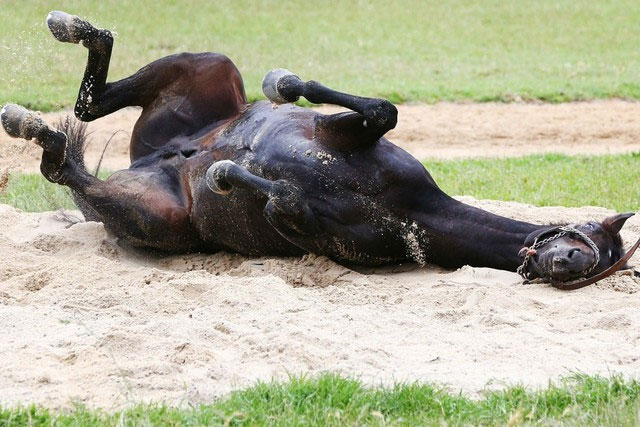

In contrast, horses face significant challenges in healing broken legs. The peculiarities of their bone structure, characterized by longer and thinner bones, make natural healing difficult. The fragility of horse leg bones, coupled with the substantial weight they bear, exacerbates the challenge.
Horses, as herbivores, depend on running for extended periods to find food or escape predators. A broken leg impedes their ability to run, transferring the body’s burden to the remaining legs and causing additional pain and pressure. This impediment makes recovery arduous and prolongs healing time.
Treating broken legs in horses requires substantial resources, including finances, manpower, and medications. For many, investing such resources in treating horses becomes a formidable financial burden. Technological limitations in treating horses further compound the issue, with the need for professional veterinary teams, which may not always be readily available, especially in remote areas.
The contrasting tales of elephants thriving with broken legs and horses succumbing to the same fate highlight the intricate interplay of factors in the animal kingdom. Elephants’ robust bone structure, powerful muscles, intelligence, and social bonds contribute to their resilience, while horses face challenges due to the fragility of their bones, mobility constraints, limited resources, and time constraints. Understanding these differences sheds light on the diverse survival mechanisms in nature, unveiling the mysteries of the animal world.